Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) are critical components of the immune system that elicit a response to intruders entering the human body and attack existing cells that have transformed into a cancerous cell type.
Researchers rely on human PBMCs as the “fuel” for developing new diagnostics & therapies. In today’s age of companion diagnostics, targeted therapeutics, and precision medicine, this reliance is dramatically heightened and continues to grow.
Researchers and clinicians use PBMCs to study the following areas:

Why are PBMCs important for research?
PBMC-based experiments play a key role in drug discovery, diagnostic development, cancer research and gene therapy. In vitro PBMC studies are ubiquitous in research laboratories focused on cell biology and immunology, among other disciplines.(1)
PBMCs are also critical for in vivo studies and translational research. Scientific breakthroughs in personalized medicine have included transforming PBMC-derived immune cells into CAR-T cells used to treat certain cancers.(2) Also, PBMCs are critical for disease modeling and toxicity screening ahead of conducting human clinical trials.
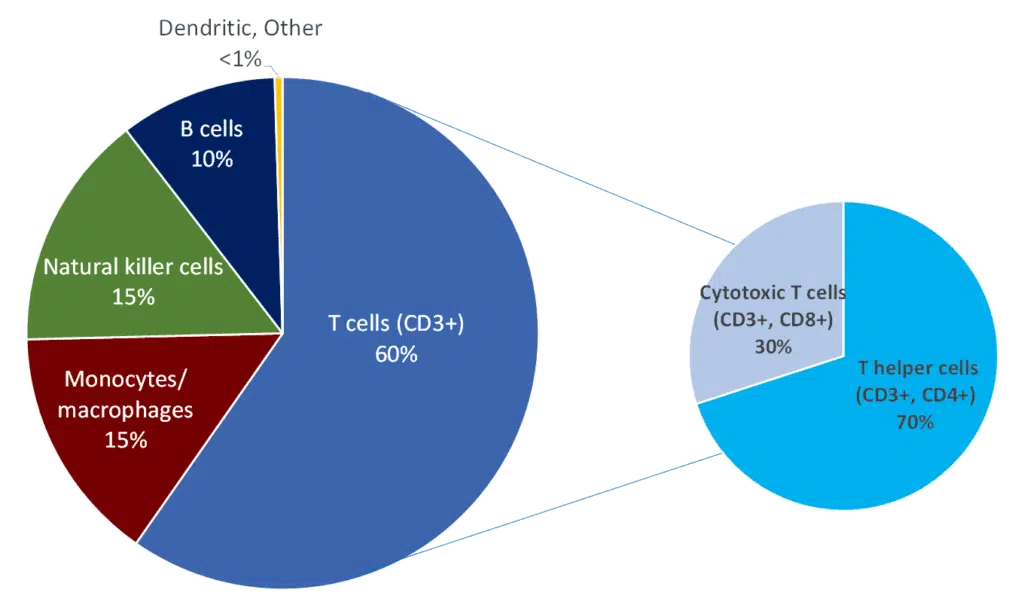
PBMCs consist of a multitude of immune cells including lymphocytes (T cells, B cells and NK cells), monocytes and dendritic cells. The isolation of these cell types is essential for many preclinical research applications and informs therapeutic decision-making in precision medicine.(3) Figure A provides a relative frequency of these immune cell populations in PBMC samples.
Figure A. Average Composition of PBMCs in a Healthy Adult Human
How are PBMCs obtained?
PBMCs are commonly isolated from whole blood or collected from donors via leukapheresis. After PBMCs are collected & isolated, a routine viability and concentration measurement is performed to confirm the quality of the sample before a cryopreservation process for storage.(4)
For the typical research lab, the isolation of PBMCs from blood is extraordinarily time-consuming and costly. Researchers must either coordinate with healthcare providers that may have access to donors from whom PBMCs may be obtained or they must recruit their own donors. Either approach can take months due to manual processes to identify donors and samples that meet research criteria. Collecting and isolating high-quality PBMCs is also a technical process that requires specialized expertise and equipment.
Cytologics offers a convenient option for researchers looking to obtain customizable, high-quality PBMCs with an industry-leading turnaround time. By using our products and services, customers can significantly accelerate their research and development programs, ultimately enabling a shorter timeline to clinical studies and eventual commercialization.
Conclusion
PBMCs are critical for preclinical research as a source of biomarkers in infectious and chronic diseases and information on the underlying mechanisms of immune response. It is important for researchers conducting in vitro and in vivo experiments to source PBMCs from a supplier that guarantees non-activated, non-contaminated (by RBCs, granulocytes) and high viability cells.
Cytologics is committed to supporting researchers and clinicians with high-quality and ethically-sourced PBMCs that lead to new treatments and diagnostics. Contact us to learn more how we can accelerate your research!
References
(1) Davis et al. (2010). Analysis of Complex Biomarkers for Human Immune-Mediated Disorders Based on Cytokine Responsiveness of Peripheral Blood Cells. J Immunol 184 (12) 7297-7304.
(2) Hartmann et al. (2017). Clinical development of CAR T cells—challenges and opportunities in translating innovative treatment concepts. EMBO Molecular Medicine 9 (9) 1183-1197.
(3) Hu et al. (2016). Single Cell Isolation and Analysis. Cell and Developmental Biology.
(4) Zhang and Huang (2012). The multi-differentiation potential of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 3 (48) 2-10.